 |
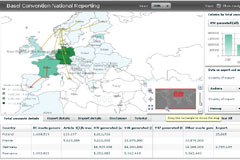
The Basel Convention data visualization tool shows interactively data provided by the Parties on generation and transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and other wastes.
Data visualization tool puts hazardous waste data at your fingertips
 This data visualization tool was created to show, in an interactive way, data provided by the Parties to the Basel Convention on generation and transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and other wastes. It contains data for the years 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2010.
The tool is fully compatible with Internet Explorer and Google Chrome. The Secretariat is working to make it also compatible with other browsers.
There is a video tutorial available in case you need help to understand how the tool works.
Should you come across any issue or erroneous data while using this site, please report it to: sbc_natrep@unep.org
Disclaimer: This tool and data is based on information transmitted in reports transmitted by Parties to the Basel Convention. The data provides an indication of trends and activities but must be carefully interpreted.
Acknowledgement: we would like to thank the United Nations Office at Geneva – Information and Communication Technology Service (UNOG-ICTS) for their collaboration in the development of this tool.
|
 |
Staff members of the Secretariat have new standardized e-mail addresses.
Secretariat of the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Conventions adopts standardized e-mail addresses
As of 15 April 2013, each of our staff members have been assigned a new e-mail address in the standard format firstname.lastname@brsmeas.org. This new format applies to all members of the Secretariat, independently of whether staff are hosted by UNEP or FAO.
In addition to this standardized address, the UNEP staff will continue using e-mail addresses in the format firstname.lastname@unep.org and the FAO staff will continue using e-mail address in the FAO format firstname.lastname@fao.org.
The e-mail addresses in the pic.int and pops.int formats will continue to be functional for six months, to facilitate the transition to the new addresses. Rest assured that messages sent to our former addresses will still be delivered.
|
 |
The number of Parties to the Convention rises to 180.
Afghanistan ratifies the Basel Convention
Afghanistan has ratified the Basel Convention, depositing its instrument of ratification with the Secretary-General of the United Nations on 25 March 2013. The Convention will enter into force for Afghanistan on 23 June 2013 in accordance with article 25 (2) of the Convention.
Afghanistan’s action raises the number of Parties to the Basel Convention to 180.
More information is available from Status of Ratifications.
|
 |
Sustainable business models key to waste reduction.
New agenda seeks to transform e-waste into opportunity
 Sustainable business models key to waste reduction.
Geneva, 2 April 2013 – Representatives of Central American governments, private companies, universities and non-governmental organizations have agreed on a 20-point Agenda aiming to promote advances in the handling of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE or ”e-waste”) in the region. Key will be the application and identification of business models that leverage recycling opportunities and create new employment.
The new Agenda was agreed by the 86 participants in the ITU/UNEP Workshop for Capacity Building on Environmentally Responsible Management of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE), organized in San Salvador, March 19-21 with the support of ITU Sector Member Telefónica.
The Agenda emphasizes increased collaboration between all parties, as well as the development of online learning programmes and workshops aimed at policy-makers. It calls on ITU and UNEP/PACE to assist Central America and the Caribbean in the development of regulations, legislation and international standards to mitigate e-waste’s potentially damaging effects on the environment and the health of local populations.
Electronic devices can contain up to 60 different chemical elements. But deficiencies in collection methods, recycling technologies and illegal dumping mean the majority of these valuable resources are lost when equipment reaches end-of-life.
The failure to close the loop on e-waste leads not only to adverse environmental impacts, but also to the depletion of a potentially valuable resource base of ‘secondary equipment’.
Dr. Hamadoun I. Touré, Secretary-General of ITU, explains that “The e-waste challenge will be met by combining effective legislation with incentives to develop business and employment opportunities to maximize the lifespan of these valuable finite natural resources. Capacity building and technology transfer to developing countries, along with the implementation of international standards, will be key to reducing waste and pollution, in parallel with the creation of sustainable business models.”
Workshop participants reaffirmed their commitment to the implementation of the Basel, Rotterdam, and Stockholm Conventions, while also recognizing the importance of ITU Resolution 79 on “The role of telecommunications / information and communication technology in handling and controlling e-waste from telecommunication and information technology equipment and methods of treating it” adopted by the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (Dubai, 2012). This resolution urges ITU to develop activities related to capacity building and the implementation of recommendations, methodologies and other publications on the responsible management of e-waste.
Speaking at the opening of the Workshop, Vice-Minister of Environment and Natural Resources of El Salvador, Ms Lina Pohl, said: “WEEE is a topic of high relevance to this region and the world. We need to act now, before it becomes an ‘unstoppable waste tsunami’ that causes irreversible damage to our health and environment.”
“The Central American Commission on Environment and Development (CCAD) is very thankful for this important contribution and happily offers to promote this Agenda and its model of cross-cutting integration of efforts amongst environment, health and telecommunication authorities, private sector and civil society,” said Mr. Nelson Trejo, Executive Secretary of CCAD, at the inauguration of the workshop.
“If we tap into the potential of wide public-private sector partnerships to promote environmentally sound management of WEEE, we will be able to create a vibrant green economy, while reducing poverty, health hazards and risks, climate change and the pressure on our non-renewable resource base,” said Mr. Miguel Araujo, Director of the Basel Convention Regional Center for Central America and Mexico (BCRC-CAM).
Note to media
The Workshop for Capacity Building on Environmentally Responsible Management of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment was jointly organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU); the Secretariat of the Basel Convention administered by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), through the Basel Convention Regional Center for Central America and Mexico (BCRC-CAM); in cooperation with the Partnership for Action on Computing Equipment (PACE) established under the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development (CCAD); and the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources of El Salvador (MARN).
For more information, please contact:
Ms. Sarah Parkes
Chief, Media Relations & Public Information ITU
Tel: +41 22 730 6039
E-mail: pressinfo@itu.int
Mr. Toby Johnson
Senior Communications Officer
Tel: +41 22 730 5877
Mobile: +41 79 249 4868
E-mail: toby.johnson@itu.int
|
 |
Join the session on best practices and policies on environmentally sound management of used and end-of-life ICT equipment, World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) 10-year Review, 26 February 2013, 16:05-17:30 Register
Avoiding e-waste: Sustainable life-cycle management of ICT equipment
Join the session on best practices and policies on environmentally sound management of used and end-of-life ICT equipment, World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) 10-year Review, 26 February 2013, 16:05-17:30 Register
|
 |
The Technical Expert Group of the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Waste and their Disposal completed a framework for the environmentally sound management (ESM) of hazardous wastes and other wastes at its third meeting, held from 21 to 23 January 2013, in Glion, Switzerland.
The framework establishes a common understanding of what ESM encompasses and identifies tools and strategies to support and promote the implementation of ESM. It is intended as a prac...
Basel Convention Technical Expert Group develops framework for environmentally sound management of wastes
The Technical Expert Group of the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Waste and their Disposal completed a framework for the environmentally sound management (ESM) of hazardous wastes and other wastes at its third meeting, held from 21 to 23 January 2013, in Glion, Switzerland.
The framework establishes a common understanding of what ESM encompasses and identifies tools and strategies to support and promote the implementation of ESM. It is intended as a practical guide for all stakeholders participating in the management of hazardous wastes and other wastes.
The framework will be considered and possibly adopted at the eleventh meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Basel Convention (COP 11) in April 2013, in Geneva, Switzerland.
|
 |
International efforts to regulate the trade in waste revolve around the Basel Convention. (Photo: Kai Loeffelbein)
"The politics of e-waste: A cadmium lining", from The Economist (26 January 2013)
International efforts to regulate the trade in waste revolve around the Basel Convention. (Photo: Kai Loeffelbein)
|
 |
From the Secretariat of the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Conventions
Season’s Greetings and Best Wishes for the New Year 2013
From the Secretariat of the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm Conventions

|
|
The Technical Expert Group fleshed out the scope of a new framework for the environmentally sound management of hazardous wastes and other wastes at its second meeting, held from 30 September to 2 October 2012, in Geneva. The framework is intended as a practical guide for all stakeholders participating in the management of hazardous and other wastes.
Technical Expert Group works to develop framework for environmentally sound management of hazardous wastes and other wastes
The Technical Expert Group mandated to develop a framework for the environmentally sound management (ESM) of hazardous wastes and other wastes fleshed out the scope, objectives and guiding principles of the new framework at its second meeting, held from 30 September to 2 October 2012, in Geneva.
Twenty-four of the 30 international experts nominated by Parties were joined by 18 observers to continue work on the framework that was initiated in Tokyo in April 2012.
The Group agreed that the framework is intended as a practical guide for all stakeholders participating in the management of hazardous and other wastes. The framework will establish a common understanding of the elements of ESM through the provision of standards, criteria andguidelines, define tools to support and promote their implementation and identify strategies to overcome challenges.
The Group discussed what are the main challenges related to the implementation of ESM, among them ensuring a uniform interpretation of ESM, tackling the vexing problem of illegal traffic and ensuring the development of adequate national capacity for ESM.
One further meeting will be held (scheduled from 21 to 23 January 2013 in Glion, outside of Montreux, Switzerland) to further progress the development of the framework which will be considered and possibly adopted at COP 11 of the Basel Convention in April 2013.
|
 |
ICC approves compliance action plans and allocates funding from Basel Convention implementation fund.
Implementation and Compliance Committee works through parties’ difficulties in complying with national reporting obligations
 The ninth meeting of the Basel Convention Implementation and Compliance Committee took place on 8-9 November 2012 in Geneva, Switzerland.
Following consideration of nine specific submissions, the Committee adopted decisions aimed at resolving each Party's difficulties in implementing and complying with its national reporting obligation. In two of these instances (Bhutan and Togo), the ICC took the unprecedented step of approving compliance action plans and allocated funding from the Basel Convention implementation fund (up to USD 50’000.- each) to undertake activities listed therein. The ICC also considered general issues of implementation and compliance and agreed on conclusions and recommendations pertaining to national legislation, national reporting, illegal traffic, inventories, the control system, as well as insurance, bond and guarantees.
The meeting was chaired by Ms Jimena Nieto (Colombia) and welcomed the attendance of 13 Committee members, three Parties concerned by a specific submission, namely Oman, Bhutan and Togo, as well as a representative of Switzerland in its capacity as President of the eleventh meeting of the Conference of the Parties.
More
|
 |
Technical guidelines on environmentally sound co-processing of hazardous wastes in cement kilns adopted by the Parties to the Basel Convention at COP10 are available in English, French and Spanish
Co-processing of selected waste streams in properly controlled cement kilns provides energy, material recovery and cost effective options for industry and waste generators
|
 |
As a follow up to the CLI decision requesting the Secretariat to promote cooperation between existing enforcement networks, a meeting of enforcement networks and enforcement organizations hosting enforcement networks was held on 2-3 October 2012 in Geneva, Switzerland.
Meeting of Enforcement Networks
As a follow up to the CLI decision requesting the Secretariat to promote cooperation between existing enforcement networks, a meeting of enforcement networks and enforcement organizations hosting enforcement networks was held on 2-3 October 2012 in Geneva, Switzerland.
|
 |
Geneva, Switzerland, 25 - 28 September 2012.
Documents pertaining to the meeting will be posted on the Basel Convention website as they become available.
Eighth meeting of the Open-ended Working Group of the Basel Convention (OEWG 8)
Geneva, Switzerland, 25 - 28 September 2012.
Documents pertaining to the meeting as well as additional information will be posted on the Basel Convention website as they become available.
|
 |
The meeting of the Basel and Stockholm convention regional centres was held from 1 to 2 Oct 2012, followed by a joint meeting with FAO and UNEP regional offices on 3 Oct 2012.
Joint meetings of the Basel and Stockholm convention regional centres and FAO and UNEP regional offices
The meeting of the Basel and Stockholm convention regional centres was held from 1 to 2 Oct 2012, followed by a joint meeting with FAO and UNEP regional offices on 3 Oct 2012.
|
 |
Expanded Bureau makes preparations for upcoming ordinary and extraordinary meetings of the Conference of the Parties.
Expanded Bureau agrees to COP-11 provisional agenda
Expanded Bureau makes preparations for upcoming ordinary and extraordinary meetings of the Conference of the Parties.
|
 |
The technical guidelines to properly manage wastes consisting of elemental mercury and wastes containing or contaminated with mercury aim to protect human health and the environment.
Technical guidelines for the environmentally sound management of wastes with mercury
The technical guidelines to properly manage wastes consisting of elemental mercury and wastes containing or contaminated with mercury aim to protect human health and the environment.
|
|
The Working Group will consider several scientific and technical, legal and strategic matters, including the development of the technical guidelines on transboundary movement of e-waste, in particular regarding the distinction between waste and non-waste; development of the technical guidelines on persistent organic pollutants; and the proposals for new entries to the list of wastes contained in Annex IX to the Basel Convention submitted by Finland, Ireland, and the Netherlands.
Basel Convention Open-ended Working Group to review framework for environmental sound management of wastes
The eighth meeting of the Open-ended Working Group of the Basel Convention is being held from 25 to 28 September 2012 at the Geneva International Conference Centre (CICG), in Geneva, Switzerland.
The Open-ended Working Group keeps under continuous review the implementation of the Convention’s work plan, specific operational policies and decisions taken by the Conference of the Parties for the implementation of the Convention. It meets once every two years.
The Working Group will consider several scientific and technical, legal and strategic matters, including the development of the technical guidelines on transboundary movement of e-waste, in particular regarding the distinction between waste and non-waste; development of the technical guidelines on persistent organic pollutants; and the proposals for new entries to the list of wastes contained in Annex IX to the Basel Convention submitted by Finland, Ireland, and the Netherlands.
As a follow-up to the Indonesian-Swiss country-led initiative to improve the effectiveness of the Basel Convention adopted at COP10 of the Convention, a progress report on the development of guidelines for environmentally sound management of waste will be provided, and the report on the interpretation of certain terminology to provide further legal clarity will be considered.
The outcomes of the meeting will help set the stage for the 11th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Basel Convention, which will be held back-to-back with the conferences of the parties to the Rotterdam and Stockholm conventions during a two-week period from 28 April to 10 May 2013 in Geneva. These back-to-back conferences will be held for the first time in tandem with an extra-ordinary meeting of the conferences of the parties charged with solidifying synergies among the three conventions.
|
 |
The benefits of ship dismantling, or recycling, derive from the materials and equipment comprising end-of-life ships, whose scrap steel, mechanical parts and other valuable equipment are recycled or refurbished for use in other industries. End-of-life ships also comprise of an array of hazardous materials – such as asbestos, PCB and waste oils – which can have serious implications for the environment and human health if not managed properly.
Concern over ship dismantling practices prompts capacity building initiatives
 The benefits of ship dismantling, or recycling, derive from the materials and equipment comprising end-of-life ships, whose scrap steel, mechanical parts and other valuable equipment are recycled or refurbished for use in other industries. End-of-life ships also comprise of an array of hazardous materials – such as asbestos, PCB and waste oils – which can have serious implications for the environment and human health if not managed properly.
Concern has been expressed at the international level over the environmental, health and safety standards in this industry, particularly in those countries employing the beaching method of ship recycling. Ship recycling commonly takes place in developing countries which tend to have a competitive advantage as they provide a pool of low cost labour, may have weaker environmental protection / worker health and safety regulations, and have national demand for the outputs of the activity (predominantly scrap steel). Poor enforcement of regulations relating to this activity means that problems with local environmental pollution are commonplace and incidents of worker injury and fatality are high. These concerns are compounded given the upward trend in recycling activity experienced in the past few years.
The Basel Convention has been involved in the issue of ship dismantling for over a decade and works at the policy and technical levels and through its capacity building programme toward improving environmental, health and safety standards in this important industry.
|
 |
Vital Waste Graphics 3 charts global trends and sheds light on the obstacles that prevent the practical implementation of waste minimization, recycling and resource recovery.
UN report graphs global waste challenges
 A new report, Vital Waste Graphics 3, charts global trends and sheds light on the obstacles that prevent the practical implementation of policies to promote waste minimization, recycling and resource recovery.
Vital Waste Graphics 3 covers a wide-range of waste-related topics, including preventive tools for wastes; the market for clean-up and treatment of hazardous waste and recycling of scrap metals; biogas and compost; solid waste management; waste external costs to health, biodiversity, climate change, and land use; producer and consumer responsibility; food waste; green procurement; disasters and waste; waste crime and illegal traffic.
The report’s message is presented through more than 70 charts and graphs that reveal, explain and communicate connections between the environment and society.
Vital Waste Graphics 3 draws and maps a broader vision of the present and for the future, in order to raise awareness of the costs and consequences of generating waste, and the opportunities of minimizing and managing it in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
Already, the livelihoods of 15 million people worldwide – and one to two percent of the urban population in some developing countries – depend on waste picking or the scavenging of waste. Protective measures for waste workers and nearby inhabitants, pollution control systems and risk mitigation measures are often insufficient in low-income countries.
Manufacturing products according to “green design” principles which integrate environmental and health considerations into their design, improved product labeling and certification of waste are among the measures that could protect health and environment, boost recycling rates, and contribute to turning waste into revenue and resources for other economic activities.
Vital Waste Graphics 3 is available here.
|
 |
The UNEP Secretariat of the Basel Convention is pleased to announce that it is joining the Partnership on Measuring ICT for Development.
Basel joins the Partnership on Measuring ICT for Development
 Port Louis, Mauritius (7 December 2011) – The UNEP Secretariat of the Basel Convention is pleased to announce that it is joining the Partnership on Measuring ICT for Development.
In a statement issued on the opening day of the International Telecommunication Union’s World Telecommunications/ICT Indicators Meeting on 7 December 2011, Mr Torbjorn Fredriksson, Chief of the ICT Analysis Section of the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) said,
“The inclusion of the Basel Convention Secretariat is particularly valuable at a time when growing attention is being paid to the measurement of the environmental implications for ICT, such as the growth of electronic waste “ said the current chair of the Partnership Steering Committee.
“The Secretariat of the Basel Convention will bring to the Partnership on Measuring ICT for Development its expertise and experience with e-waste issues on global level, its network of national and international institutions, academics, industry and civil society,” commented Mr Matthias Kern, who will be representing the Basel Convention Secretariat in the Partnership.
“Measuring e-waste is one of the emerging topics we are exploring at this year’s World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators Meeting. I am extremely pleased to announce the new membership of the UNEP Secretariat of the Basel Convention at this occasion,” said Ms Susan Teltscher, Head of ITU’s ICT Data and Statistics Division.
ITU, the Basel Convention Secretariat and the United Nations University are conducting a joint online survey on e-waste – https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/ewastesurvey2011 – through 31 January 2012.
|
 |
This publication is an element of the E-waste Africa programme, which aims at enhancing the environmental governance of e-wastes and creating favourable social and economic conditions in the recycling sector in Africa.
Launch of new publication (executive summary) "Where are WEEE in Africa"
 A new publication related to e-waste has been launched at the side-event “Experiences in environmentally sound management of e-waste in Africa and Asia-Pacific” which take place on 20 October 2011 during the Tenth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Basel Convention, 17 - 21 October 2011 in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia.
The results and findings presented in this publication have been generated in the framework of the Basel Convention E-waste Africa programme, which aims at enhancing the environmental governance of e-wastes and creating favourable social and economic conditions for partnerships and small businesses in the recycling sector in Africa. The initial phase of the programme consists of the E-waste Africa project and complementary activities triggered by the project and implemented by partner organizations. Following completion of the E-waste Africa project, follow-up activities are expected to be carried out supporting countries in the region to tackle e-waste issues.
The overarching goal of the E-waste Africa project is to enhance the capacity of West Africa and other African countries to tackle the growing problem of e-waste and thereby protect the health of citizens, particularly children, while providing economic opportunities. Specifically, the project aims to improve the level of information available on flows of EEE and e-waste imported into West African countries; assess the baseline situation in terms of amounts of EEE imports, EEE in use and e-waste in partner countries, as well as environmental impacts of the e-waste sector; study the social-economic aspects of the increasing volumes of used EEE and e-waste; and strengthen national capacities to monitor and control transboundary movements of e-waste and to prevent illegal traffic.
The publication serves to share knowledge generated through the several studies and activities of the E-waste Africa project primarily with stakeholders in the project partner countries, but also with stakeholders in other African countries and those who are concerned with the e-waste issue and are interested in seeking sustainable solutions: imports, collection and recycling, policy and legislation, and enforcement.
You can download the executive summary of the publication.
For more information, you can visit the E-waste Africa Project page.
|
|
The new Strategic Framework for 2012-2021 should enable the Basel Convention to highlight the links between waste management and the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals. The draft strategy sets out a vision, guiding principles, strategic goals and objectives, as well as means of implementation and indicators of achievement.
New Strategic Framework and Indonesian-Swiss Country Led Initiative aim to improve the effectiveness of the Convention
The new Strategic Framework for 2012-2021 should enable the Basel Convention to highlight the links between waste management and the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals. The draft strategy sets out a vision, guiding principles, strategic goals and objectives, as well as means of implementation and indicators of achievement.
Linked in substance with the Strategic Framework is the outcome of the Country-Led Initiative (CLI) by Indonesia and Switzerland. Launched in response to the call of the President of COP9 to find a way out of the controversy surrounding the Ban Amendment, the CLI proposes a set of measures to break through the deadlock holding up entry into force of the Amendment. Their adoption could constitute a historic step towards a solution after over 15 years of blockage.
The New Strategic Framework will be considered for adoption at COP10 in Cartagena, Colombia on 17–21 October 2011.
|
 |
The promise of “synergies” between the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm conventions took another supple step forward this month with the opening of the new Basel Convention website.
Basel Convention website advances synergies
 The promise of “synergies” between the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm conventions took another supple step forward this month with the opening of the new Basel Convention website, the third “leg” of the conventions’ joint clearing-house family of websites.
The Basel website will be officially launched during COP10 in Cartagena, Colombia, 17–21 October 2011. The new Stockholm and Rotterdam websites were launched at their respective COPs held earlier this year.
The launch of the new Basel website completes the integration of the Basel Convention’s web information into the joint clearing house. The entrance to each of the conventions’ websites is through a common gateway page, expressing a harmonized design while sporting an individual ‘look and feel’.
The Basel website is framed in a shamrock green, setting it off from Rotterdam’s navy blue and Stockholm’s striking orange pages. The Basel web address familiar to long-time users of the website –www.basel.int –has been kept.
Basel now shares a common architecture with its sister sites, starting with quick links to frequently requested ‘Meetings’, ‘Documents’, ‘Networks’, ‘Projects’ and ‘Publications’ which are found at the top of the page of each home page.
A comprehensive drop down menu guides users to implementation and country-specific chapters organized by activity or topic.
Information about the ‘Convention’, the ‘COP’ and subsidiary bodies, ‘Compliance’ and ‘Media’ are also collected under a single heading, with additional chapters introducing the ‘Secretariat’ and major ‘Partners’.
As the centrepiece, the website presents four featured articles. Further sections offer ‘ In the spotlight’ , ‘Announcements’, ‘Activities’, ‘Upcoming Meetings’ and ‘Webinars’.
One test of synergies is how the newly designed communication tools impact work on the ground. The goal is to support implementation of the conventions at the national level by bringing improved coherence in information exchange and to the organization of information resources that ease the burden on Parties and the public to find what they need.
With the opening of the Basel clearing-house website, we hope to bring the Basel community a step closer to realizing this goal.
|
 |
Mr. Jim Willis, a US national, took up his position as Executive Secretary of the Secretariat of the Basel Convention, Stockholm Convention Secretariat and UNEP-part of the Rotterdam Convention Secretariat on 18 April 2011.
Appointment of the new Executive Secretary
Mr. Jim Willis, a US national, took up his position as Executive Secretary of the Secretariat of the Basel Convention, Stockholm Convention Secretariat and UNEP-part of the Rotterdam Convention Secretariat on 18 April 2011.
Mr. Willis has throughout his distinguished career worked in the field of environment with particular focus on policy issues related to chemicals and wastes. Mr. Willis worked as the Director of the Chemical Control Division with the US Environmental Protection Agency (2004-2011) and previously as the Director of the UNEP Chemicals Branch (1995-2004), which included serving as Executive Secretary of the Rotterdam and Stockholm conventions' secretariats.
|